Cloud computing is the delivery of a diverse range of IT services via the Internet. It harnesses an array of resources, including data storage, servers, databases, networking capabilities, and software applications.
Cloud computing adopts an innovative approach to using resources spread remotely, thereby allowing any electronic device connected to the internet to access data and software.
Unlocking the Essence of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing derives its name from the idea of storing data and resources remotely in a virtual space known as a "cloud." Using cloud services, consumers can effortlessly store files and applications on remote servers and subsequently access their data through the internet. The beauty of this arrangement is that users are not confined to a specific location or device to gain access; they can work remotely from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud computing liberates devices from the burden of heavy processing, allowing you to work with lighter, more efficient systems. By shifting the workload to vast computer clusters situated in a remote cyberspace, the cloud provides enhanced computational power and scalability, enabling seamless data management and analysis.
More importantly, cloud computing enables cost savings, increased productivity, speed, and efficiency, along with secured workflows.
Cloud Deployment Models
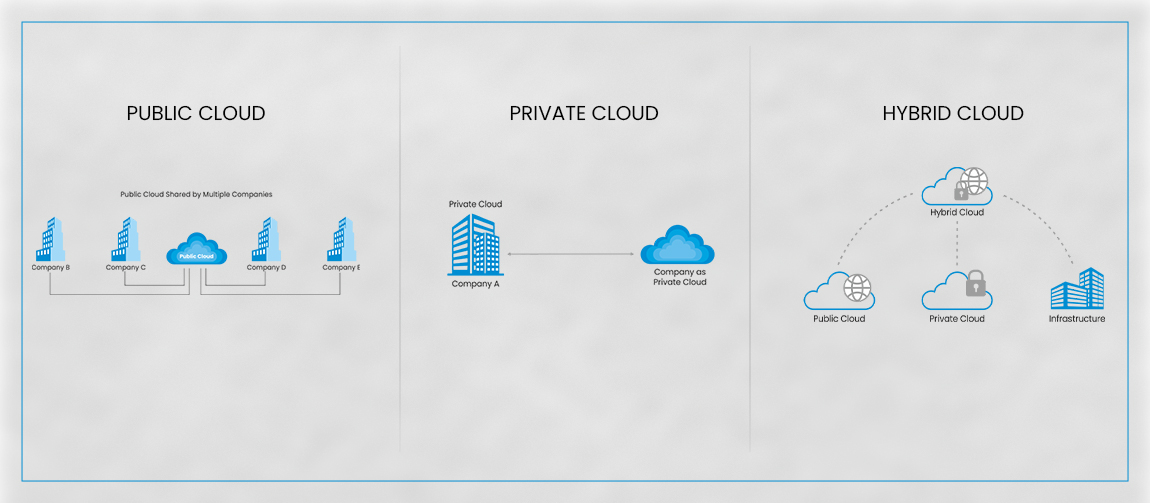
• Public Cloud: Public cloud entails the provisioning of resources by a third-party provider over the internet, accessible to both organizations and individuals seeking to utilize or acquire them. Within this framework, certain resources are accessible at no cost, while others can be obtained through subscription or pay-as-you-go payment structures.
• Private Cloud: A private cloud denotes a cloud computing setting exclusively reserved for an organization. The foundational computing elements of a cloud infrastructure, such as processing power and storage, are commissioned and made available via a self-service gateway. In private clouds, all these resources remain segregated and under the governance of a single organization. Private clouds come with the inherent benefits of faster delivery and flexibility. They also allow customers to maintain the same level of security and access control that is available on on-premise infrastructure.
• Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid cloud solutions strive to amalgamate private and public cloud systems, combining a dedicated organizational computing environment with resources from the public cloud. These hybrid configurations empower enterprises to opt for either private or public settings tailored to particular applications and tasks, all while reaping the advantages of streamlined administration spanning both domains.
Types of Cloud Services
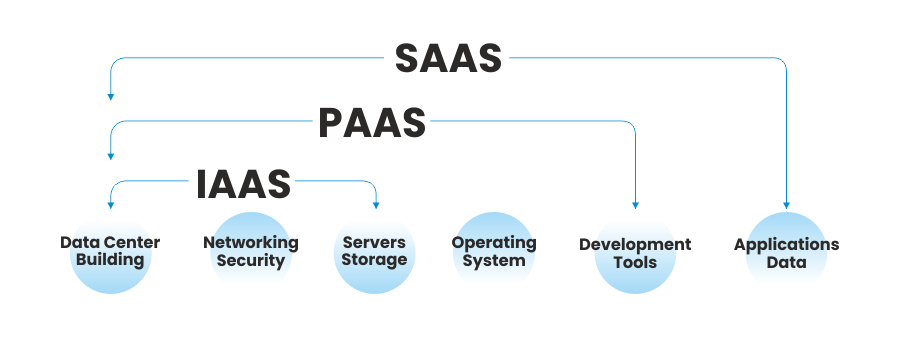
IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service)
Infrastructure-as-a-Service, often abbreviated as "IaaS", represents a variant of cloud service wherein essential computing, networking, and storage resources are provided to consumers on-demand and on a pay-as-you-go basis over the internet. IaaS empowers consumers to readily scale or shrink resources as required, mitigating the necessity for substantial initial investments or unwarranted ownership of infrastructure, especially in instances of unpredictable and flu0ctuating workloads.
PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service)
Platform-as-a-Service, also abbreviated as “PaaS”, represents a cloud service that provides customers access to a complete cloud platform: hardware, software, and infrastructure to develop, run, and manage applications. This model relieves consumers of the cost, complexity, and inflexibility of building and maintaining the platform on-premise. The PaaS provider takes charge of all components: servers, networks, storage, operating system software, databases, and development tools, housing them within their data center. Normally, customers have the option to pay a fixed fee for a designated quantity of resources catering to a specific user count. Alternatively, they can opt for 'pay-as-you-go' pricing, remitting solely for the resources they actively utilize.
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service)
Software-as-a-Service, also known as “SaaS”, is a computing model that allows on-demand access to ready-to-use, cloud-hosted application software. Consumers pay a monthly or annual fee to use a complete application, wherein all the infrastructure required to manage the software-servers, storage, networking, middleware, application software, and data storage is managed by the SaaS provider. Thus, the SaaS provider ensures the availability, performance, and security of application software for consumers.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
• Scalable & Flexible : Cloud computing allows for scaling computing resources and storage to meet business demands without requiring upfront investments in physical infrastructure. At the same time, the usage can be scaled down as and when required, offering much needed flexibility.
• Efficient : Cloud-based applications are accessible from anywhere on any internet connected device. Also data security is not restricted by hardware failures because of networked back-ups. Remotely placed computing resources available at all times, accessible on a “pay-as- you-go” model, provides more operational efficiency to organizations and also saves costs of commissioning and maintaining servers and other equipments.
• Cost Effective : Irrespective of the cloud service model you opt for, your charges correspond exclusively to the resources you actively employ. This helps avoid excessive infrastructure construction and provisioning in data centers, allowing IT resources additional time to concentrate on higher-level strategic endeavors.
• Secure : Contrary to common beliefs, cloud computing has the potential to enhance your security stance due to its comprehensive range of security functionalities, automated upkeep, and centralized administration. Esteemed cloud providers also recruit leading security specialists and implement cutting-edge solutions, thereby providing heightened and more resilient protection.
Considerations While Adopting a Cloud Computing Partner
Selecting the right cloud service integrators is essential to ensure the successful integration and management of your cloud solutions. Here are important factors to consider before making your decision:
• Security and Compliance : Though cloud computing is secure, it is always advisable to the cloud service provider for security and compliance levels. Assess the provider's security measures, data encryption protocols, and compliance certifications to ensure your data will be adequately protected and in line with industry regulations.
• Performance & Reliability : Evaluate the provider's track record in terms of uptime, latency, and overall system performance. Look for built-in redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure high availability.
• Partnerships & Certifications : Check if the integrator holds certifications your chosen cloud provider and partnerships that reflect adequate technological knowhow.
• Support and Maintenance : Verify the integrators post-implementation support and services to ensure your solution remains operational and optimised.
LUBI as your Trusted Cloud Partner
LUBI Electronics is an automation solutions provider pioneering in providing solutions in integrating factory data on Azure and AWS. We also provide solutions for managing your cloud based database helping you assimilate and analyze data on- the- go.
Conclusion
Cloud computing offers heightened flexibility,dependability and efficacy, alongside cost reduction in managing data. It serves as a catalyst for innovation, facilitating quicker time-to-market and the integration of AI and machine learning applications into organizational strategies. This can lead to ancillary benefits, bolstering productivity, enabling remote workforces, and refining operational efficiency.

